Why am I telling you this? I believe your company could be the next victim if you don’t have a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy in place. I am aware that medium and large companies have an IT department and a number of IT security processes. But a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy should go beyond that. Here are the top five reasons why every company should have a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy to prevent cyber attacks and limit their consequences.
1. A growing part of business is taking place on the Internet
More and more business activities are taking place in cyberspace. Every sector and every company of all sizes is affected by digitization. Companies and customers have gone online at a rapid pace. There are over 3.2 billion Internet users worldwide today, which is 40 percent of the world’s population (according to Internet Live Stats ).
More and more business transactions are being carried out using mobile devices such as smartphones or tablets. Of the 3.65 billion mobile users, 1.9 billion use smartphones (source: Statista ). The value of global eCommerce via mobile devices is growing correspondingly rapidly – in the second quarter of 2014 it was 130 billion dollars (source: Statista ).
As eCommerce continues to grow at a rapid pace, it becomes increasingly important to ensure that eCommerce is secure. The importance of cybersecurity grows even further when you think of emerging business trends such as the smart, connected home and eHealth.
2. The number and intensity of cyber attacks are increasing
Parallel to the growing number of Internet users and eCommerce transactions, the number and intensity of cyber attacks are also increasing. There is no reliable comprehensive data. But data from some surveys confirm the statement. In a 2014 survey conducted by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) , 77 percent of respondents said that cyberattacks increased between 2013 and 2014, and 82 percent said it was likely or very likely that their company would be attacked in 2015 .
According to the same survey, cyber threats came from cyber criminals (46 percent), non-malicious insiders (41 percent), hackers (40 percent) and malicious insiders (29 percent) in 2014.
The cost of these attacks to the affected companies was significant. A study by the Ponemon Institute puts the average cost at $ 7.7 million per organization per year, ranging from $ 0.31 million to $ 65 million.
3. Customer trust is based on data integrity
Every business is based on the trust of its customers. In the case of business conducted via the Internet, this trust is based in principle on the integrity of the customer data and how well it is protected by the company. Put yourself in the customer’s shoes: would you rather buy from a company that was recently hacked, like VTech, or one that wasn’t?
Given the evolving business scenarios around the Internet of Things, where you have a lot of networked devices in the home and at work, an effective cybersecurity strategy is a prerequisite for building and maintaining customer trust, whether B2C or B2B.
4. Cyber security is more than an IT department job
In a number of organizations, cybersecurity is primarily treated as a task for the IT department. IT professionals are expected to take technical measures to ensure that their company’s digital business is protected from cyber attacks.
However, this approach has fundamental weaknesses. Leaving the IT department to deal with cyber threats is not enough. Cybersecurity is a challenge for the boardroom, not just the computer room.
Cybersecurity affects the whole company and should be treated accordingly.
5. Workers can be either a security risk or a strength
Cybersecurity is just as much a personnel issue as it is an IT issue.
Many cybersecurity risks are created or exacerbated by inattentive employees. Take the loss of mobile devices, for example. It represents a major security risk, because data found on these devices could provide access to sensitive company data. In the aforementioned ISACA survey, 83 percent of companies equipped their employees with mobile devices, and 91 percent of those companies reported losing mobile devices in 2014.
This example shows that employee behavior is an essential security factor that should be considered in a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. Such a strategy should include building awareness of the dangers, user training and incentives for employees to behave responsibly when handling digital data and communication devices.
It should also include against the effects of some workers who knowingly or unconsciously create safety risks. In practice, you will not achieve 100% safe behavior from all employees at all times. Therefore, you need safeguards and procedures to mitigate any risk.
Conclusion
When it comes to cybersecurity, complacency is dangerous and a degree of paranoia is healthy. It is important to have a comprehensive view of cybersecurity and develop a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. This should be an issue that should be dealt with at the boardroom level, not just the IT department. It requires executives to gain a better understanding of IT systems and IT professionals in the organization to gain a better understanding of business processes.

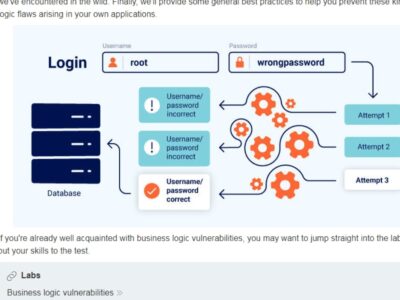



















Comments