Introduction: The Evolving World of Barcodes
Barcodes are everywhere—from supermarket shelves to hospitals, warehouses, manufacturing lines, libraries, and smartphones. These simple patterns of lines or dots are the foundation of modern logistics and supply chain management, enabling quick, error-free data capture and efficient product handling.
But what exactly makes barcode scanners so essential in 2025, and how have the technologies and types evolved? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the functions of barcode scanners, explain the latest barcode technologies, cover all common barcode types, address industry trends, and answer the most frequently asked questions.
Table of Contents
-
What Is a Barcode Scanner?
-
How Do Barcode Scanners Work?
-
The Latest Barcode Scanner Technologies (2025 Updates)
-
Most Common Barcode Types and Their Uses
-
Applications of Barcode Scanners Across Industries
-
Choosing the Right Barcode Scanner for Your Needs
-
Key Trends: AI, IoT, and Cloud Connectivity
-
Practical Examples and Case Studies
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Conclusion & Next Steps
1. What Is a Barcode Scanner?
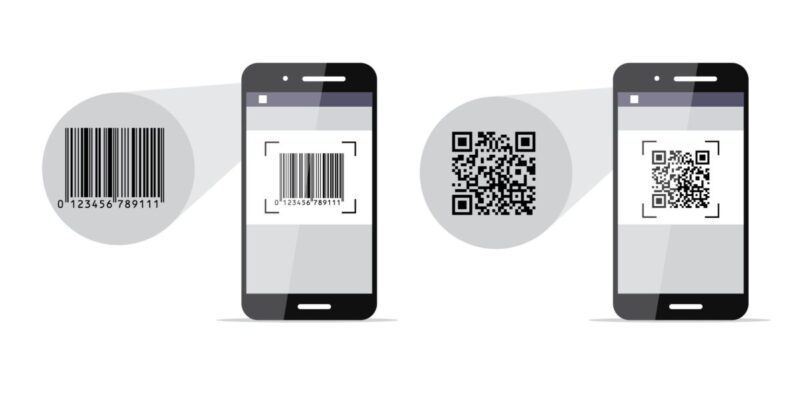
A barcode scanner is an electronic device designed to quickly read barcodes printed on labels, packaging, or digital screens. By translating visual codes into readable data, barcode scanners automate inventory tasks, streamline point-of-sale transactions, and reduce human errors.
2. How Do Barcode Scanners Work?
At its core, a barcode scanner detects the unique patterns of a barcode (either lines, dots, or shapes) using light, then decodes the information to send it to a computer or software system.
Basic Barcode Scanning Process:
-
Illumination: The scanner shines a light source (LED or laser) onto the barcode.
-
Detection: Sensors in the scanner measure the reflected light.
-
Decoding: The device’s software interprets the code pattern and converts it into digital data.
-
Transmission: The data is sent to a computer, inventory system, or point-of-sale solution.
Modern scanners use optical imagers, CCD sensors, lasers, or even smartphone cameras for this process.
3. The Latest Barcode Scanner Technologies (2026 Updates)
Barcode scanning technology has evolved significantly, especially with recent advancements in AI, IoT, and wireless communications. Here are the top innovations shaping barcode scanners in 2025:delfi+2
AI-Powered and Smart Barcode Scanners
-
AI-driven scanning: New scanners can recognize and correct for damaged or poorly printed codes using machine learning.
-
Batch processing: Scan multiple barcodes simultaneously, boosting efficiency.
-
Real-time analytics: Scanned data is processed instantly for faster business insights.
IoT and Cloud Integration
-
Wireless connectivity: Most modern devices support Wi-Fi 6, 5G, or Bluetooth for real-time syncing with cloud-based inventory systems.
-
IoT integration: Scanners can now be linked to the entire supply chain, providing live tracking and status updates.
Improved Ergonomics and Battery Life
-
Lightweight, durable designs for extended use in warehouses or retail environments.
-
Long battery life (many can last full shifts with fast-charging options).
Augmented Reality and Mobile Scanning
-
AR overlays: Some scanners now use augmented reality to display helpful info (like inventory levels) directly onto scanned items.
-
Smartphone-based scanning apps let employees use personal devices for robust 1D/2D code scanning.
Key takeaway: The best scanners today do far more than read barcodes—they boost productivity, deliver data analytics, and enable smarter logistics.
4. Most Common Barcode Types and Their Uses
Not all barcodes are created equal. Modern businesses use a range of barcode types to match specific industry and data needs.packagex+2
Linear (1D) Barcode Types
| Barcode Type | Typical Use Cases | Features |
|---|---|---|
| UPC-A/UPC-E | Retail products, supermarkets | 12 digits (US, Canada), fast retail checkout |
| EAN-8/EAN-13 | Global retail, books | International standard, 8/13 digits, high reliability |
| Code 39 | Automotive, inventory, defense | Alphanumeric, can encode letters/numbers |
| Code 128 | Shipping, logistics, healthcare | Compact, supports letters, numbers, special chars |
| ITF (Interleaved 2 of 5) | Cartons, distribution | Numeric only, good for bulk packaging |
| Codabar | Libraries, photo labs | Numeric, used for consecutive numbering |
| Barcode Type | Typical Use Cases | Features |
|---|---|---|
| QR Code | Advertising, mobile payments | Stores up to 4,000 chars, scan with smart devices |
| Data Matrix | Electronics, small items | Up to 2,000 chars in small spaces, high error correction |
| PDF417 | Airline tickets, ID cards | Highly secure, encodes large datasets, multi-row |
5. Applications of Barcode Scanners Across Industries
Barcode scanners are central to operations in virtually every major industry. Here’s a look at some of the most impactful real-world uses:
Retail and Point of Sale
-
Fast checkout: UPC/EAN scanning for quick, accurate sales.
-
Stock management: Automated reordering and live stock updates.
Warehousing and Inventory
-
Automated goods tracking: Every shipment tracked from arrival to dispatch.
-
Permanent inventory control: Never run out of essential stock.
Manufacturing and Production
-
Automated workflow: Parts moving through production lines with minimal human intervention.
-
Error reduction: Auditable, automatic data capture reduces mistakes.
Healthcare
-
Patient safety: Scans ensure correct medication and patient identification.
-
Asset and supply management: Track medical supplies, equipment, medication.
Logistics and Shipping
-
Shipment tracking: End-to-end visibility, even allowing customers to monitor delivery status.
-
Reduced errors: AI-powered scanners quickly identify mislabeled or damaged packages.yhdaa+1
Education and Libraries
-
Book and media tracking: Fast check-in, check-out for students/librarians.
-
Student/staff ID cards: Barcode-based attendance and identification.
6. Choosing the Right Barcode Scanner for Your Needs
With so many barcode scanner options, how do you select the right one? Here’s a handy breakdown by scanner type and use case:dcodeinternational+1
Common Barcode Scanner Types
-
Laser Scanners: Fast, highly accurate—perfect for high-traffic retail or industrial applications.
-
CCD Scanners: Reliable and rugged, great for close-range and high-volume scanning.
-
Imager Scanners: Camera-based, read both 1D and 2D codes, suitable for mobile and diverse environments.
-
Pen-Type Scanners: Budget-friendly, best for low-volume, specific business needs.
-
Omnidirectional Scanners: Can scan from any angle—perfect for grocery self-checkouts and busy POS.
-
Mobile/Camera Scanners: Ideal for companies leveraging employees’ smart devices.
Checklist for Picking the Best Scanner:
-
What barcode types (1D, 2D, QR) do you need to scan?
-
Will scanners be used in retail, industrial, healthcare, or on-the-go settings?
-
Do you need wireless, Bluetooth, or IoT connectivity?
-
Is integration with cloud software or inventory management essential?
-
How many scans per day? (Consider battery life and durability)
7. Key Trends In Barcode Scanning: AI, IoT, and Cloud in 2025
Barcode scanner technology in 2025 is faster, smarter, and more integrated than ever:
-
Artificial Intelligence: AI enables smart error correction, batch scanning, and predictive analytics.
-
IoT Connectivity: Cloud-based integration brings real-time data sharing, global inventory views, and predictive supply chain management.
-
Mobile Scanning: BYOD (bring your own device) policies leverage staff phones for dynamic scanning tasks.
-
Sustainability: Many industries now favor scanners with low energy consumption and eco-friendly designs.
-
Market Growth: The barcode scanner market is forecasted to surpass $12 billion by 2030.
Companies using AI-powered scanners saw a 30% increase in operational efficiency and a significant drop in errors (Zebra Technologies study).
8. Practical Examples and Recent Case Studies
Case Study 1: Smart Warehouse Automation
A leading e-commerce warehouse integrated IoT-enabled wireless barcode scanners connected to their inventory software. Outcome:
-
Reduced stock errors by 40%
-
Improved restocking times by 30%
-
Achieved real-time product tracking from arrival through shipment
Case Study 2: Retail Self-Checkout
A national supermarket chain replaced handheld devices with omnidirectional scanners at all self-checkout stations. Results:
-
Checkout times decreased by 25%
-
Customer satisfaction increased via fewer “unreadable barcode” errors
Case Study 3: Healthcare Inventory Management
A hospital adopted mobile imager scanners to track medicine and medical devices:
-
Medications matched to the right patients, reducing errors
-
Expired items automatically flagged for removal
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What’s the difference between 1D and 2D barcodes?
-
1D barcodes (linear) contain data in lines, like UPC and Code 39. 2D barcodes (matrix) encode info in squares or dots, holding much more data (like QR or Data Matrix codes).
2. Can barcode scanners read damaged or faded labels?
-
Yes—AI-powered scanners in 2025 can read most damaged, faded, or poorly printed codes by analyzing patterns and reconstructing missing data.
3. Is a smartphone as accurate as a dedicated scanner?
-
For occasional use, yes. Most smartphones handle QR and Data Matrix codes easily. For high-volume, industrial jobs, dedicated scanners offer more speed, reliability, and battery life.
4. How secure is barcode data?
-
Barcodes themselves are not secure, but sensitive uses employ secure transmission (like HTTPS), encryption, and/or barcode verification steps.
5. What are the main benefits of using barcodes in business?
-
Efficiency, accuracy, real-time inventory updates, error reduction, cost savings, and improved customer experiences.
6. Can scanners work with software like ERP or inventory management systems?
-
Yes—modern scanners often support standard protocols that enable plug-and-play connectivity with most point-of-sale or enterprise platforms.
7. What’s next for barcode technology?
-
Expect continued AI-driven improvements, full cloud integration, seamless mobile scanning, and richer data analytics across the value chain.
10. Conclusion
In 2025, barcodes and barcode scanners are more essential than ever, powering the fast-paced world of retail, logistics, healthcare, manufacturing, and more. Whether you need to speed up your supermarket checkout, keep perfect stock levels in your warehouse, or embrace the latest in smart scanning technology, understanding barcode fundamentals will give your business a competitive edge.
Ready to upgrade your operations or need guidance on the best barcode scanning solution for your needs?
Contact us today or explore our in-depth product guides for expert advice!
- https://shop.delfi.com/en/the-latest-innovations-in-wireless-barcode-scanners-in-2025
- https://www.yhdaa.com/blog/navigating-2025-technology-trends-for-bar-code-scanners/
- https://www.scandit.com/blog/choosing-the-right-barcode-scanner/
- https://packagex.io/blog/barcode-types
- https://codecorp.com/about/blog/what-are-the-most-common-barcode-types/
- https://www.activebarcode.com/codes/
- https://www.dcodeinternational.in/blog/barcode-scanner-uses-guide-2025/
- https://www.honeywell.com/us/en/news/featured-stories/2019/11/interesting-facts-about-barcode-scanners
- https://www.logiscenter.eu/news/most-common-barcode-types
- https://www.netsuite.com/portal/resource/articles/inventory-management/barcode.shtml


















Comments